Colors possess diverse characteristics, encompassing hue, saturation, brightness, and gloss, and they result from the reflection of light reaching our eyes. However, each individual perceives colors differently. For instance, one person may perceive a particular dress as black and blue, whereas another may see it as white and gold.
The same variability applies to how different screens display and reproduce color. Most displays have limitations on the range of colors they can generate, and each device adheres to one or more color standards that define its specific color gamut. While numerous color gamuts are available, it is likely that there is one that best suits your requirements.
So what exactly is color gamut? Which one do you need on your monitor? Find out in our article below.
Color Gamut
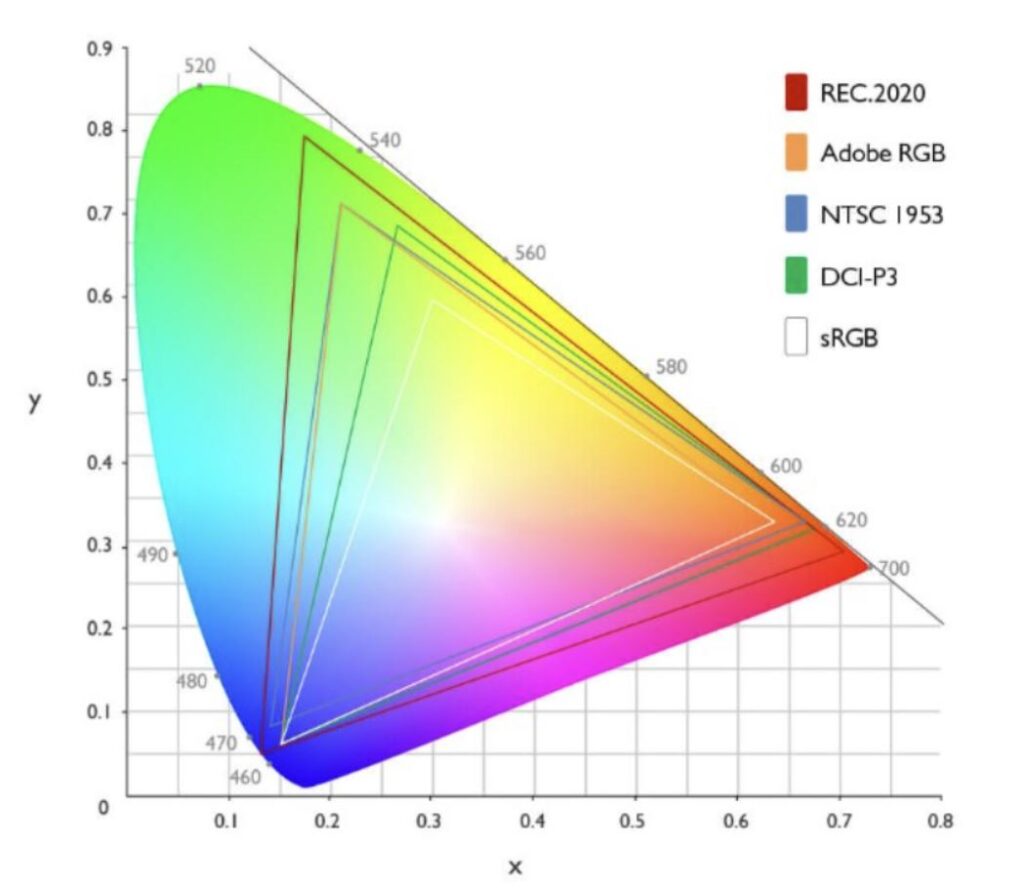
The color gamut represents a spectrum or color space that defines the range of colors that can be reproduced on a given output device. The extent of this gamut determines the variety of colors displayed on a screen. While the majority of monitors can produce around 16.7 million colors, there are those capable of achieving a significantly broader range.
When shopping for a television or monitor, several factors catch your attention. Alongside the physical size and dimensions, you also focus on the colors displayed within the images. The presence of deep blacks, vibrant reds and greens, and other captivating colors can make a significant impact. A visually stunning demonstration showcasing rich and lifelike colors might be the deciding factor between merely browsing and becoming a customer.
However, it’s important to avoid confusing color gamut with resolution, as it can be tempting to equate them. It’s understandable since color quality and overall quality may appear not only interconnected but interchangeable. Keeping that in mind, the representation of color and how it varies between products is directly influenced by factors such as color gamut, color coverage, and the various color standards in place.
Color Standards
sRGB & What High % in this mean for the average consumer?
Higher percentages in sRGB (Standard Red Green Blue) generally mean better color reproduction and a more vibrant and accurate display of images and videos. sRGB is a widely adopted color space that ensures consistent color representation across different devices, such as monitors, printers, and cameras.
When a monitor advertises a higher percentage coverage of sRGB, it indicates that the monitor can display a larger portion of the sRGB color gamut. The sRGB color gamut represents a specific range of colors that can be reproduced. A higher percentage coverage means the monitor is capable of displaying a larger number of colors within that range.
In practical terms, a higher percentage coverage of sRGB can result in more accurate and lifelike colors. If you’re working with images or videos that are specifically designed for sRGB color space, a monitor with higher sRGB coverage can provide a more faithful representation of the original content. It can be particularly important for tasks that require color accuracy, such as photo editing, graphic design, or video production.
However, it’s worth noting that sRGB is just one color space, and there are other wide color gamuts like Adobe RGB and DCI-P3 that offer even larger color ranges. If you work with content specifically designed for these wider color spaces, you might want to consider monitors that cover those gamuts instead.
DCI-P3 & What High % in this mean for the average consumer?
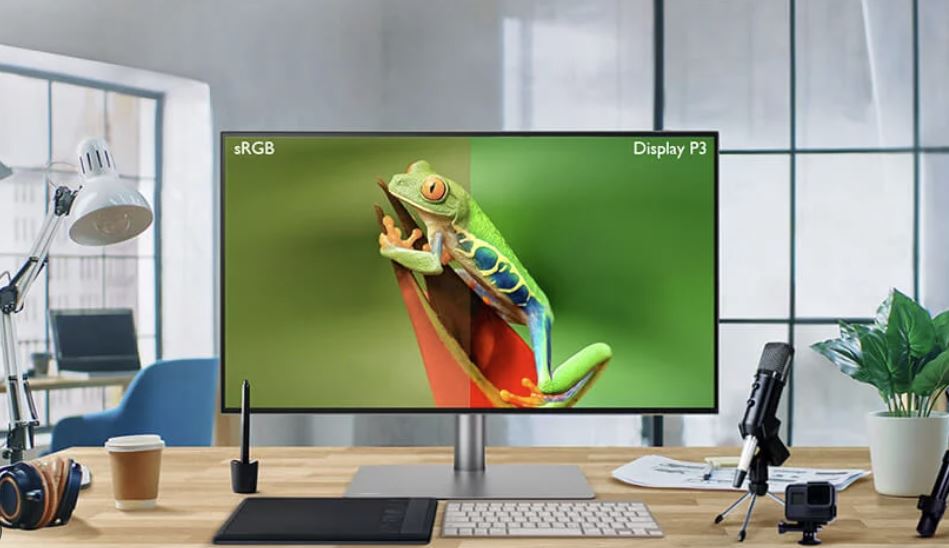

Higher percentages in DCI-P3 (Digital Cinema Initiatives – P3) refer to the color gamut or color range that the monitor can display. The DCI-P3 color space is a standard used in the film industry, primarily for digital cinema projection.
When a monitor has a higher percentage coverage of the DCI-P3 color space, it means that it can reproduce a wider range of colors, including more vibrant and saturated shades. This is particularly beneficial when viewing content that has been mastered in the DCI-P3 color space, such as certain movies, videos, or games.
If you’re an average consumer, having a monitor with a higher percentage of DCI-P3 coverage can enhance your viewing experience by providing more accurate and vivid colors. It allows you to see content as intended by the content creators, especially if it has been optimized for the DCI-P3 color space.
However, it’s important to note that not all consumer content is mastered in the DCI-P3 color space. Most consumer-grade content, such as websites, photos, and videos, is typically created using the sRGB color space, which has a narrower color range compared to DCI-P3. Therefore, unless you specifically work with DCI-P3 content or have a preference for more vibrant colors, a high percentage of DCI-P3 coverage may not be essential for your average day-to-day usage.
NTSC & What High % in this mean for the average consumer?
In the context of monitors, the reference to higher percentages in NTSC typically refers to the color gamut coverage.
NTSC (National Television System Committee) is a color standard used in analog television broadcasting.
The NTSC standard defines a specific range of colors that can be displayed on a television or monitor. When a monitor specifies a higher percentage of NTSC coverage, it means that the monitor is capable of displaying a larger range of colors.
For an average consumer looking to buy a monitor, higher percentages in NTSC can be an indication of better color reproduction and a more vibrant and accurate display. However, it’s important to note that NTSC is an older standard and not widely used in modern monitors. Nowadays, most monitors use other color gamut standards such as sRGB or Adobe RGB.
When evaluating monitors, you should look for color gamut specifications such as sRGB (standard Red Green Blue) or Adobe RGB coverage percentages, as they are more relevant and widely accepted in the industry. These standards provide a more accurate representation of color reproduction, especially for tasks like photo editing, graphic design, or content creation.
In summary, while higher NTSC percentages may suggest better color reproduction, it’s advisable to focus on monitors with higher coverage percentages in widely recognized and more relevant color gamut standards like sRGB or Adobe RGB.
Adobe RGB & What High % in this mean for the average consumer?
Adobe RGB is a color space that is used in the digital photography and graphics industry to represent a wide range of colors.
Monitors that support Adobe RGB can display a larger range of colors than monitors that only support the more common sRGB color space.
For the average consumer looking to buy a monitor, a higher percentage in Adobe RGB may not necessarily mean a significant improvement in color accuracy or quality. This is because most consumer-grade devices, such as digital cameras and smartphones, capture images in the sRGB color space. As a result, if you are primarily using your monitor to view images from these devices, you may not notice a significant difference in color quality between a monitor that supports Adobe RGB and one that only supports sRGB.
However, if you work in the photography or graphics industry and regularly use software such as Adobe Photoshop or Lightroom, a monitor that supports Adobe RGB can be beneficial. This is because it allows you to work with a larger range of colors, resulting in more accurate color representation and better color grading. In this case, a higher percentage in Adobe RGB can indicate that the monitor is capable of displaying a wider range of colors, which can be important for professional work.
In summary, if you are an average consumer who uses their monitor mainly for everyday tasks such as browsing the internet, watching videos, and playing games, a monitor that supports sRGB should be sufficient. However, if you work in the photography or graphics industry, a monitor that supports Adobe RGB may be worth considering, and a higher percentage in Adobe RGB can indicate a more capable monitor.
EBU & What High % in this mean for the average consumer?
When referring to higher percentages in EBU, it likely relates to the EBU Tech 3320 standard, which specifies the recommended settings for monitors used in professional video production.
The EBU standard defines certain parameters, including brightness, contrast, color gamut, and color accuracy, that monitors should adhere to in order to ensure consistent and accurate video reproduction.
Higher percentages in EBU measurements indicate that a monitor meets or exceeds these recommended standards.
It’s worth noting that EBU standards are primarily targeted at professional applications, such as broadcast television and video production. For most average consumers, a monitor that meets the standard sRGB color space and provides good overall image quality should suffice for everyday use, including web browsing, multimedia consumption, and casual gaming.
REC & What High % in this mean for the average consumer?
Higher percentages in REC refer to the color gamut coverage of the monitor.
Rec. 709 is a standard that defines the color space for high-definition television (HDTV) and is widely used in the industry.
Rec. 709 has a specific color gamut defined, which is narrower than some other color spaces like DCI-P3 or Adobe RGB. When a monitor advertises a higher percentage coverage of Rec. 709, it means that the monitor is capable of displaying a larger portion of the colors defined within that standard. So, for the average consumer, higher percentages in Rec. 709 mean that the monitor can reproduce a wider range of colors, resulting in more vibrant and accurate color representation.
This can be particularly important for tasks like photo editing, graphic design, where color accuracy and vibrancy are desired.
However, it’s worth noting that the perception of color can be subjective, and the specific color needs may vary depending on the user’s preferences and use cases. Additionally, if you require a wider color gamut for professional tasks such as print production or video editing, you might want to consider monitors that cover larger color spaces like DCI-P3 or Adobe RGB.
Conclusion
Generally speaking, if you are an average consumer who uses their monitor mainly for everyday tasks such as browsing the internet, watching videos, and playing games, a monitor that supports sRGB should be sufficient.
Higher DCI-P3 coverage should only be considered if the media content you enjoy is geared towards a DCI-P3 Monitor or if you enjoy greater color saturation.
The other standards are only important for professionals, involved in photo/video editing, graphic design or in the case of Adobe RGB, using specific Adobe Software Products, for color accuracy and grading.
Additionally, keep in mind that while higher sRGB, DCI-P3 coverage is generally desirable, other factors like color calibration, contrast ratio, and panel technology also play a role in determining the overall quality of the display.
Finally consider your specific needs, such as the type of content you usually consume and your budget, when choosing a monitor. Other factors like resolution, refresh rate, response time, and connectivity options are also crucial to consider alongside color gamut for an optimal viewing experience.



