In today’s digital era, choosing the right monitor is crucial for an optimal visual experience. When exploring the market, you’ll encounter various panel types, each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
In this article, we will delve into the key differences between some of the most popular monitor panel types available: IPS, Nano IPS, VA, TN, OLED, and QLED. By understanding their characteristics, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs.
Traditional Panels
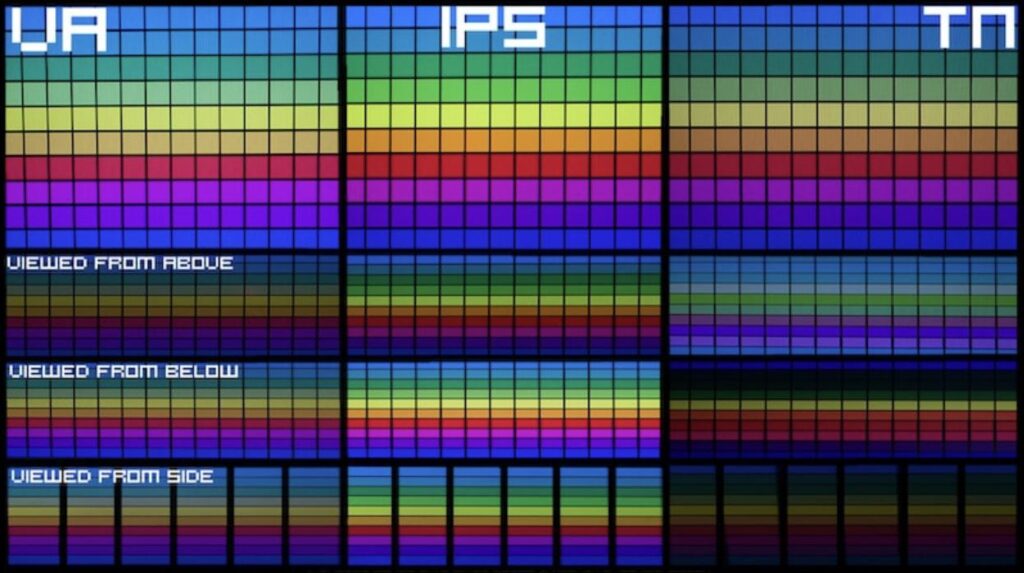
Vertical Alignment
(VA)
VA panels strike a balance between IPS and TN technologies. They provide better contrast ratios and deeper blacks than IPS displays, making them suitable for watching movies or playing games that require dark scenes.
VA panels offer wider viewing angles compared to TN displays but are generally not as wide as IPS panels. The response times of VA panels fall between those of IPS and TN, making them a good compromise for gaming and multimedia purposes.
However, VA panels may suffer from “ghosting” effects in high-motion scenarios.
In-Plane Switching
(IPS)
Renowned for their exceptional color accuracy, wide viewing angles, and good overall image quality. With IPS technology, each pixel is aligned horizontally, ensuring vibrant colors and minimal color shifting when viewed from different angles. These panels are ideal for professionals working in design, photo editing, or content creation, as they offer accurate color representation.
However, IPS panels generally have a slower response time compared to TN panels, which can result in motion blur in fast-paced gaming scenarios.
Twisted Nematic
(TN)
TN panels are known for their lightning-fast response times, making them a popular choice for gaming enthusiasts. They offer high refresh rates, which reduce motion blur and deliver smooth gaming experiences. TN panels are also relatively inexpensive compared to other panel types.
However, TN displays often have limited viewing angles, and the colors may appear washed out or distorted when viewed from the side. This makes them less suitable for tasks that require precise color reproduction or collaborative work.
New Technology
Nano In-Plane Switching (Nano IPS)
Nano IPS is a variation of IPS technology that incorporates nano-sized particles in the panel’s color filters. This technology improves color accuracy and provides a wider color gamut than traditional IPS panels. Nano IPS displays are well-regarded for their precise color reproduction and excellent viewing angles. They are commonly used in professional applications that demand accurate color representation, such as graphic design or video editing. However, Nano IPS monitors may be more expensive compared to standard IPS displays.
Organic Light-Emitting Diode (OLED)
OLED panels utilize self-emitting organic compounds, resulting in individual pixels that can emit their own light. This technology delivers exceptional contrast ratios, true blacks, and vibrant colors. OLED panels offer near-perfect viewing angles and fast response times, making them suitable for both gaming and professional applications. However, OLED monitors tend to be more expensive than other panel types, and there may be concerns about potential image retention or burn-in with static content over time.
Quantum-dot Light-Emitting Diode (QLED)
QLED panels combine LED backlighting with quantum-dot technology to enhance color accuracy and brightness. These displays offer a wider color gamut than traditional LED panels, resulting in richer and more vivid colors. QLED monitors are well-suited for content creation, gaming, and HDR (High Dynamic Range) content. They generally have good viewing angles and fast response times. However, it’s important to note that QLED is a marketing term coined by Samsung, and different manufacturers may use slightly different implementations of quantum-dot technology.
Conclusion
When selecting a monitor, understanding the differences between panel types is essential.
IPS panels excel in color accuracy and wide viewing angles, making them suitable for professional tasks that require accurate color reproduction.
TN panels, on the other hand, offer fast response times and high refresh rates, making them ideal for gaming enthusiasts seeking smooth and responsive gameplay.
VA panels strike a balance between the two, providing deeper blacks and better contrast ratios than IPS panels while still offering wider viewing angles compared to TN displays.
Nano IPS panels, a variation of IPS technology, provide even better color accuracy and wider color gamut than standard IPS displays, making them a popular choice for professional applications that demand precise color representation.
OLED panels deliver exceptional contrast ratios, true blacks, and vibrant colors, making them an excellent choice for both gaming and professional applications. However, they tend to be more expensive and may have concerns about image retention or burn-in over time.
QLED panels enhance color accuracy and brightness using quantum-dot technology, offering a wider color gamut and vibrant visuals, particularly in HDR content.
Ultimately, the choice of monitor panel type depends on your specific needs and preferences. Consider the tasks you’ll be performing most frequently, whether it’s gaming, content creation, or professional work, and prioritize the qualities that matter most to you, such as color accuracy, viewing angles, response times, or contrast ratios.
By understanding the characteristics and differences between IPS, TN, VA, OLED, QLED, and Nano IPS panels, you can make an informed decision when purchasing a monitor that best suits your requirements, ensuring an immersive and visually pleasing experience.



