When it comes to purchasing a new monitor, most consumers focus on factors like screen size, resolution, and refresh rate. However, another crucial aspect that significantly impacts the overall user experience is the monitor’s response time and latency.
In this article, we will explore what these terms mean, why they matter, and how the average consumer can make informed decisions when choosing a monitor.
The Impact of Latency
Latency, often referred to as input lag, is the delay between when a signal is sent to the monitor and when it is actually displayed. It is measured in milliseconds as well and is influenced by several factors, including signal processing, image rendering, and the monitor’s internal circuitry. High latency can cause noticeable delays between user input (e.g., mouse movements or button presses) and the corresponding on-screen actions. For gamers, particularly those engaged in competitive play, low latency is crucial to ensure accurate and responsive gameplay.
Response Time
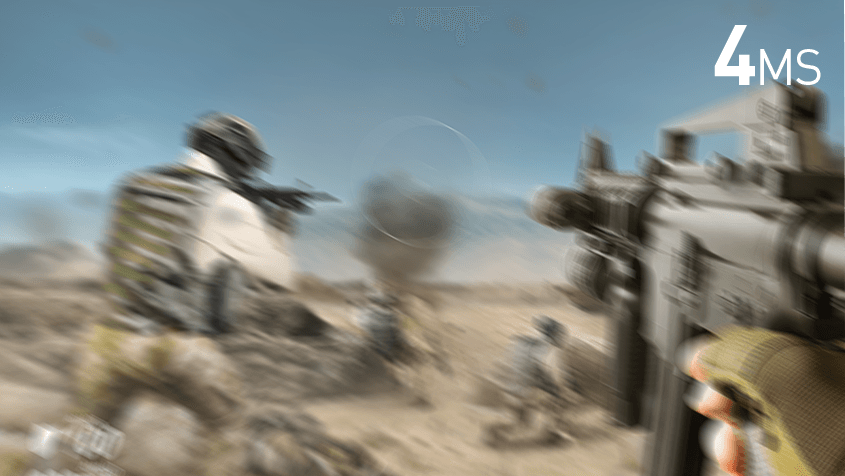

Response time refers to the speed at which a monitor’s pixels transition from one color to another. It is typically measured in milliseconds (ms) and plays a vital role in determining how quickly images and videos refresh on the screen. Lower response times indicate faster transitions and result in reduced motion blur, especially in fast-paced content such as gaming or action-packed movies.
Black to White to Black
The standard indicator for response time is the transition from black to white to black. This method measures the time it takes for a pixel to go from fully active (white) to inactive (black) and then back to active again. By measuring this time, we can determine how quickly the pixel can change colors. In the case of LCD monitors, it refers to the speed at which the liquid-crystal rises and falls, encompassing the entire transition.
Response times measured using the black to white to black method generally tend to be higher, indicating slower shifts between colors. These response times are more suitable for everyday computer users who prioritize monitor ergonomics.
Gray-to-Gray (GtG)
Gray-to-gray (GtG) response times operate based on a middle gradation, where pixels do not reach a fully inactive state. LCD monitors with GtG response times typically have around 256 gradations of gray. These response times are significantly faster and are highly suitable for individuals seeking improved gaming experiences and videography.
The measurement method for GtG response times is worth mentioning as well. Unlike the round trip total time measurement of black to white to black, GtG response times are determined by selecting several time sequences and calculating their average. This average represents the total time, measured in milliseconds, it takes for a pixel to transition from one color to another.
For the Average Consumer
For the average consumer, a monitor with a response time of 5ms or less is considered ideal. Such monitors effectively eliminate motion blur, providing smooth visuals during everyday tasks like web browsing, video streaming, or casual gaming. However, it’s worth noting that the human eye has limitations, and beyond a certain threshold, the differences in response times become less noticeable for most users.
Regarding latency, the aim should be to choose a monitor with minimal input lag. While high-end gaming monitors often advertise ultra-low latencies of 1ms or lower, these extreme levels might not be necessary for the average consumer. Monitors with latencies of around 10ms or below are generally considered satisfactory for most non-competitive use cases.
For Gamers & Gaming Purposes
If gaming is a significant priority, a monitor with both low response time and low latency is crucial to deliver an immersive and responsive gaming experience. Look for monitors specifically designed for gaming, often labeled as “gaming monitors” or with features like “adaptive sync” or “fast refresh rates.” These monitors often come with technologies such as AMD FreeSync or NVIDIA G-Sync, which help synchronize the monitor’s refresh rate with the GPU’s output, resulting in smoother gameplay and reduced tearing.
How is it different from Refresh Rate?
The refresh rate refers to the frequency at which a monitor updates its displayed image per second and is measured in hertz (Hz). A higher refresh rate results in smoother picture quality. The refresh rate is directly associated with the monitor or display hardware.
However, it is important to ensure a combination of both a good refresh rate and frame rate to achieve optimal performance. Having a high refresh rate alone may not be sufficient; a consistent and high frame rate is also necessary for a smooth and fluid visual experience.
Conclusion
Response time and latency are crucial factors to consider when choosing a monitor, even for the average consumer. While a low response time contributes to smoother visuals, low latency ensures minimal delays in on-screen actions. By aiming for a monitor with a response time of 5ms or less and a latency of around 10ms or below, the average consumer can enjoy an enhanced viewing experience during everyday tasks.
Gamers, on the other hand, may benefit from investing in monitors specifically designed for gaming, featuring even lower response times and latencies.
Ultimately, striking a balance between performance and budget will help consumers make informed decisions when purchasing a new monitor.



